Chain of Thought: AI's New Reasoning Revolution
New AI models learn to "show their work" with step-by-step transparency.How-To
Chain of Thought (CoT) reasoning is quickly becoming a standard feature in AI systems, offering users a peek into how decisions are made. As AI systems become more integrated into our daily lives, understanding how they reach their conclusions becomes even more important.
This Chain of Thought (sometimes called "Reasoning") is exactly what it sounds like. It's an AI’s ability to lay out its internal logic step by step, much like how a teacher might talk through a tough math problem step-by-step for a class.
This kind of reasoning makes AI show its work in real time. Instead of simply generating a final output, the AI breaks down its thinking process into discrete steps that you can follow. That can include splitting the task into manageable sub-problems, working through each step logically, considering alternatives, and finally presenting an answer.
Where to find Reasoning AI
Several major AI platforms have put Chain of Thought reasoning right in front of our eyes.
DeepSeek's DeepThink feature provides easy access to Chain of Thought reasoning. And it's one of the reasons DeepSeek is so popular (besides being free to use).
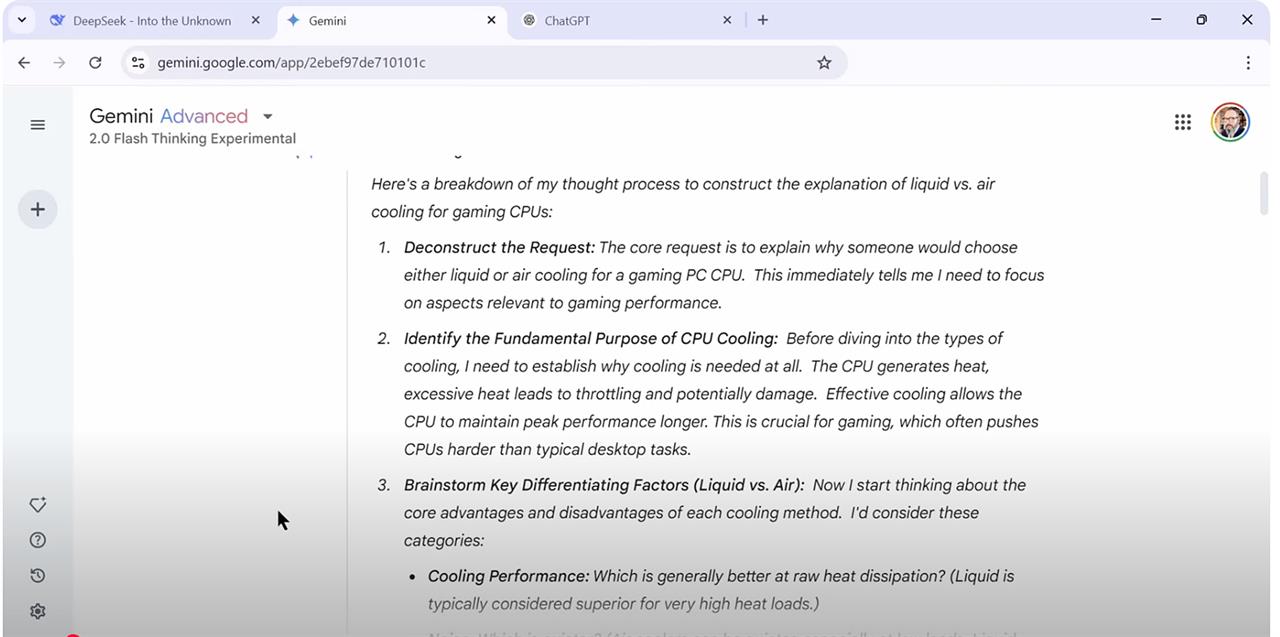
Gemini models, including Advanced 2.0, include a dedicated "Thinking" mode that shows you its multi-step reasoning process, but requires a subscription.
Some OpenAI models are adding visible CoT reasoning, including the o3-mini model, but in that case you're actually getting a summary of the off-screen reasoning. OpenAI describes what you're getting as, "an additional post-processing step where the model reviews the raw chain of thought, removing any unsafe content and then simplifies any complex ideas."
I tried the models listed above, asking a simple PC building question and seeing how the answers were constructed. My initial prompt was: "Explain to me why you'd want to choose liquid cooling or air cooling for a desktop PC CPU meant for gaming."
Excerpts from these AI interactions are below, and you can also see a real-time demo in the video above.
DeepSeek was casual and chatty in its initial reasoning, starting by saying:
"Okay, the user wants to know why someone would choose liquid cooling versus air cooling for a gaming PC CPU. Let me start by recalling the basics of both cooling methods. First, air cooling uses a heatsink and fan. It's simpler, right? Liquid cooling uses a pump, radiator, and liquid coolant. So, maybe the main factors are performance, noise, cost, and aesthetics?"
Google's Gemini went right into breaking down the component parts of my request:
"The user wants to understand the reasons for choosing liquid or air cooling specifically for a gaming desktop PC CPU. This immediately tells me I need to focus on the gaming context and explain the pros and cons of each type of cooling relative to that use case."
ChaptGPT's reasoning, at least as shown, didn't add a ton to the conversation, and felt like the least illuminative of the bunch.
"The user wants an explanation of why you'd choose liquid or air cooling for a gaming CPU. I’ll provide a balanced discussion of the pros and cons. Liquid cooling is more effective at dissipating heat, quieter, and great for overclocking. However, it's more expensive and has potential leak risks. Air cooling, on the other hand, is cost-effective, reliable, but can be bulky and noisier. I’ll break it down with factors like performance, cost, noise, and installation."
Why is CoT important?
At first glance, Chain of Thought reasoning might seem like a nice-to-have gimmick to make AI tools feel more user-friendly. But it can also build trust. When users can see how an AI arrived at a conclusion, they’re more likely to trust its output, or can spot mistakes as they happen, giving you a chance to correct those errors and avoid flawed output.
However, it also leaves you with a lot more text to go through, almost answering the questions twice, in a typically wordy style. Fortunately, the CoT display can be hidden or toggled away if you don't want to deal with it, or just want to eyeball it quickly.
As these tools evolve, Chain of Thought reasoning is likely to become a standard feature rather than a novelty. AI companies are already looking for ways to make the thought process even more intuitive, by adding visual aids, interactive elements, and natural language, to at least make it feel like AI is thinking in a very human-like way.
This apparent thinking process is ultimately an illusion, but an illusion that serves an important purpose: to bridge the gap between algorithmic processing and human understanding.
Read more: AI Tools and Tips
- How to Use an AI Agent
- DeepSeek's New AI Challenges ChatGPT — and You Can Run It on Your PC
- How To Improve Your AI Chatbot Prompts
- How I Turned Myself into an AI Video Clone for Under $50
- What is Meta AI? A Capable Chatbot That’s 100% Free
- How to Get Started with Copilot for Microsoft 365
- Getting started with LM Studio: A Beginner's Guide
- Meet Claude, the Best AI You've Never Heard of
Micro Center Editor-in-Chief Dan Ackerman is a veteran tech reporter and has served as Editor-in-Chief of Gizmodo and Editorial Director at CNET. He's been testing and reviewing laptops and other consumer tech for almost 20 years and is the author of The Tetris Effect, a Cold War history of the world's most influential video game. Contact Dan at dackerman@microcenter.com.