Breadcrumbs
Wi-Fi 6 vs. Wi-Fi 5: Understanding the Differences
As the number of connected devices in our homes grows, understanding the differences between Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) and Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) is essential for maintaining fast, efficient, and reliable wireless performance. This guide compares the two standards in terms of speed, capacity, range, and use cases—helping you choose the best option for your streaming, gaming, and smart home needs while also previewing what’s ahead with Wi-Fi 7.Buying Guides

When it comes to picking the right networking equipment, your choice of Wi-Fi standard makes a bigger difference than you might think. From streaming 4K movies and gaming online to managing dozens of smart devices, your wireless connection affects how smoothly everything runs.
Wi-Fi 5 (also known as 802.11ac) has been the workhorse of home networks for years. But Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), released in 2019, brings important upgrades—especially in speed, efficiency, and the ability to handle multiple devices at once.
In this guide, we'll break down the key differences between Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 so you can make an informed decision when shopping for networking equipment. Stay tuned, because in an upcoming article, we'll be going into detail about Wi-Fi 7.
What Are Wi-Fi Standards?
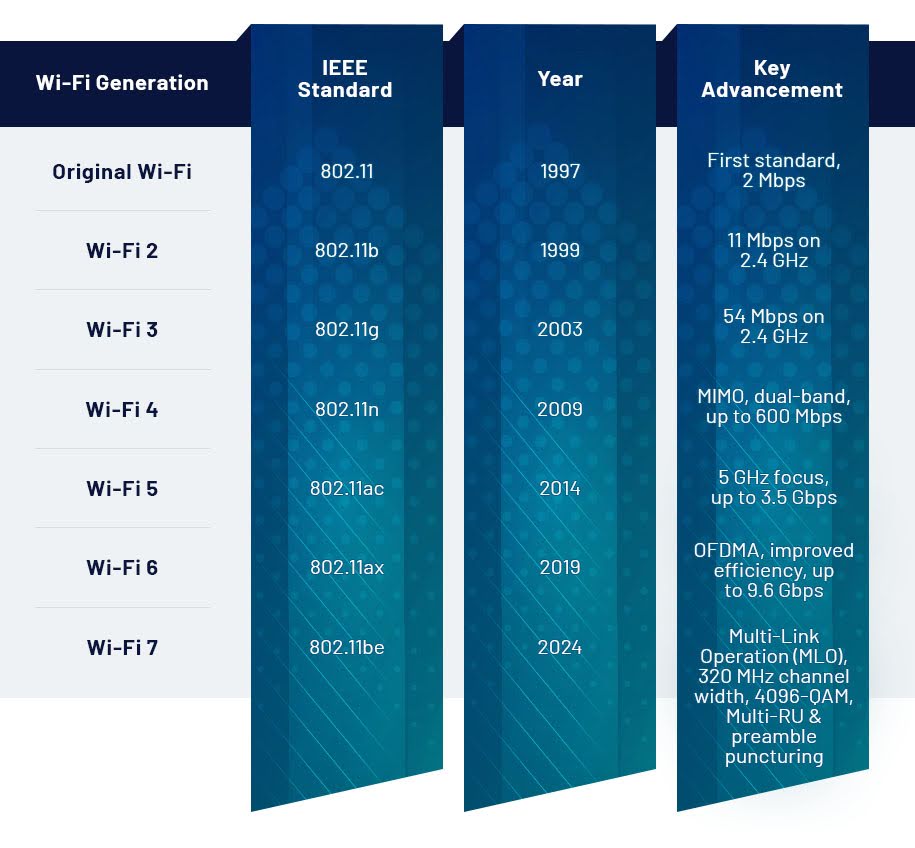
Wi-Fi standards are the technical blueprints that guide how wireless devices connect and communicate. Created by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), these standards fall under the 802.11 family and have names like 802.11ac or 802.11ax.
To make things easier for consumers, the Wi-Fi Alliance introduced simpler names. Here's how the modern generations line up:
- Wi-Fi 4: 802.11n, released in 2009
- Wi-Fi 5: 802.11ac, released in 2014
- Wi-Fi 6: 802.11ax, released in 2019
- Wi-Fi 7: 802.11be, released in 2024
Each new generation brings faster speeds, better efficiency, and stronger support for multiple devices. That's why understanding Wi-Fi5 vs Wi-Fi6 is more than just a tech spec—it's a practical decision that affects your streaming, gaming, and smart home setup.
Here's a quick look at how Wi-Fi technology has evolved over time:
As our reliance on wireless devices has grown, so has the demand for faster, more efficient standards. Today's networks need to support dozens of devices, reduce latency, and handle high-bandwidth applications. If you're looking into how to choose a router, understanding these generations is a smart place to start.
Key Features of Wi-Fi 5
Wi-Fi 5 was a major step forward in home networking, offering faster speeds and better performance than earlier generations. It set the foundation for modern wireless use, from HD streaming to smart home connectivity.

Speed and Performance
Introduced in 2014, Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) brought a noticeable jump in wireless performance. It operates on the 5 GHz frequency band and supports speeds up to 3.5 Gbps, far faster than the previous generation's 600 Mbps cap. That speed made it ideal for 4K streaming, video conferencing, and light online gaming.
One of the key technologies behind this boost is 256-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), which packs more data into each signal. Combined with wider channel widths, Wi-Fi 5 helped deliver faster and more reliable performance for common household tasks.
Bandwidth
Wi-Fi 5 improved how data flows through your network. It introduced channel bonding, which allows it to use wider 160 MHz channels. Think of it like adding more lanes to a highway—more data can move at once, which helps boost speed.
However, Wi-Fi 5 uses single-user MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output). This means your router can only talk to one device at a time, even if it's capable of high speeds. When multiple devices are connected, the router has to take turns, which can slow things down during busy times.
Beamforming was another step forward. Instead of broadcasting the signal equally in all directions, Wi-Fi 5 focuses it toward your devices. That means better range and more stable connections—especially useful in homes with multiple rooms.
Use Cases
Wi-Fi 5 works well in households with a moderate number of devices and standard internet use. It's a solid choice for:
- Streaming HD or 4K video
- Casual online gaming
- Web browsing and social media
- Remote work and video calls
- Smart homes with fewer connected devices
If you have 5-10 devices and mostly stream, browse, or work online, Wi-Fi 5 is likely enough. But as homes fill with more smart tech, the difference between Wi-Fi 5 vs Wi-Fi;6 becomes more noticeable—especially during peak hours when devices compete for bandwidth.
When you're upgrading your router or modem, it's worth thinking about how many devices your network needs to support now—and in the near future.
Key Features of Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) is built for the way we use the internet today—with more devices, heavier data loads, and higher performance demands. Upgrading to a wired or wireless router that supports Wi-Fi 6 can dramatically improve your network's speed, efficiency, and reliability.

Speed and Performance
With theoretical speeds reaching up to 9.6 Gbps, Wi-Fi 6 offers nearly three times the maximum data rate of Wi-Fi 5. That translates into faster file transfers, smoother 4K and 8K streaming, and more responsive experiences in cloud gaming or VR environments.
Much of this speed boost comes from advanced 1024-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), which allows Wi-Fi 6 to pack more data into each signal than Wi-Fi 5's 256-QAM. For a closer look at how these improvements work under the hood, IEEE's overview of the Wi-Fi 6 standard offers a useful technical breakdown.
While most users won't hit the maximum speed limits, real-world upgrades from Wi-Fi 5 often result in 30–40% faster connections, especially in busy households with multiple active devices.
Efficiency and Capacity
Wi-Fi 6 doesn't just move data faster—it moves it smarter. Two key technologies help it manage multiple devices more efficiently:
- MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output): Unlike Wi-Fi 5, which could only send data to one device at a time, Wi-Fi 6 routers can talk to up to eight devices simultaneously, in both directions.
- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access): This allows each transmission to be split into smaller chunks and shared across devices. It's like turning a single delivery route into a carpool, getting more done with less traffic.
Another upgrade, Target Wake Time (TWT), helps reduce power consumption on battery-powered devices. It lets connected gadgets schedule when they'll check in with the network, which lowers overall congestion and improves battery life for smartphones, smartwatches, and IoT sensors.
Improved Range and Reliability
Wi-Fi 6 operates on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. This dual-band approach gives you better speed at close range while also improving coverage throughout the home. Devices that are farther from the router—or blocked by walls and furniture—still benefit from stable, usable connections.
It also introduces BSS Coloring, a feature that helps routers identify and ignore signals from neighboring networks. This reduces interference in crowded environments like apartment buildings and condos, where multiple Wi-Fi networks often overlap.
The result? Fewer dead zones, more consistent speeds, and a more reliable connection throughout your space.
Range vs. Speed: Managing Expectations
When you're chasing top‐end throughput, it's easy to assume you'll get those blazing speeds everywhere in your home. In practice, though, raw speed and real-world coverage often work against each other. As you move farther from the main router:
- Connection often falls back to 2.4 GHz: Even on a tri-band system, distant rooms are most likely to stay online via the slower 2.4 GHz band rather than the high-speed 5 GHz or 6 GHz links.
- Mesh satellites halve backhaul throughput: While mesh extenders can fill dead zones, each wireless satellite unit typically delivers only about 50 percent of the router's maximum speed—so your phone or laptop may see far lower rates than the main node.
- Wired access points win for consistency: If uniform, top-speed coverage across every room is a must—especially in large or multi-story homes—a PoE-powered wired access point delivers the most reliable performance without the trade-offs of wireless backhaul.
Below are typical indoor/outdoor ranges you can expect with Wi-Fi 6 hardware (real-world results will vary by building materials and interference):
- 2.4 GHz (Wi-Fi 6): Up to 150 feet (46 meters) indoors and 300 feet (92 meters) outdoors
- 5 GHz (Wi-Fi 6): Up to 75 feet (23 meters) indoors and 200 feet (61 meters) outdoors
- 6 GHz (Wi-Fi 6E): Up to 60 feet (18 meters) indoors with minimal wall penetration
Understanding these range-vs-speed trade-offs will help you choose whether to lean on dual/tri-band routers, invest in a mesh system, or run Ethernet-backed access points to meet both your coverage and performance needs.
Use Cases
Wi-Fi 6 is especially valuable in households and workplaces with many connected devices or high bandwidth demands. It's ideal for:
- Smart homes with connected thermostats, cameras, and appliances
- Remote work setups that require video conferencing and file sharing
- 4K and 8K streaming on multiple devices simultaneously
- Cloud gaming and virtual reality applications with low-latency requirements
- Apartments or shared living spaces with overlapping networks
- Large-scale IoT environments with many simultaneous connections
If you're comparing Wi-Fi 5 vs Wi-Fi 6, the benefits of Wi-Fi 6 become increasingly clear as device counts grow and bandwidth use intensifies.
Benefits of Upgrading to Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 offers a significant boost in speed, capacity, and efficiency, making it a smart choice for modern households and businesses. Whether you're streaming, gaming, or managing a smart home, Wi-Fi 6 ensures a smoother and more reliable connection.

Future-Proofing Your Network
As digital demands grow—with higher-resolution streaming, cloud gaming, and emerging technologies like augmented and virtual reality—Wi-Fi 6 provides the necessary infrastructure to keep up. Its theoretical speeds of up to 9.6 Gbps ensure that your network won't become a bottleneck as internet service plans offer faster speeds. Pairing a Wi-Fi 6 router with a high-performance wired router can further enhance network stability and speed, especially for bandwidth-intensive tasks.
Handling Multiple Devices
Modern households often have numerous connected devices, from smartphones and laptops to smart TVs and IoT gadgets. Wi-Fi 6's technologies, such as OFDMA and expanded MU-MIMO, allow it to manage multiple connections more efficiently than Wi-Fi 5. This means smoother performance and less congestion, even when multiple devices are active simultaneously.
Enhanced Gaming and Streaming Experience
For gamers and streaming enthusiasts, Wi-Fi 6 offers reduced latency and higher data rates, leading to more responsive gameplay and smoother video playback. Cloud gaming services, which rely on consistent and fast connections, particularly benefit from Wi-Fi 6's capabilities. Similarly, streaming 4K or 8K content across multiple devices becomes more seamless, with fewer interruptions and higher quality.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Wi-Fi 6 includes a feature called Target Wake Time (TWT), which helps connected devices save energy by scheduling exactly when they need to wake up and communicate with the network. Instead of constantly staying connected and draining power, devices like smart sensors and security cameras can rest between check-ins—using less energy and extending battery life.
This is especially helpful for homes filled with battery-powered devices or mobile gadgets that spend a lot of time on standby. Even smartphones and tablets can see longer battery life in a strong Wi-Fi 6 environment.
TWT isn't just about saving battery—it also reduces strain on the network by minimizing unnecessary traffic. In fact, researchers studying Wi-Fi 6 scheduling found that coordinated wake times can lead to more efficient performance across dense device environments, improving both energy use and network responsiveness.
Choosing the Right Wi-Fi Standard for Your Needs
Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 each offer solid performance, but the best choice depends on your specific setup. The more devices, speed, or coverage you need, the more Wi-Fi 6 stands out as a worthwhile upgrade.
Here's a quick side-by-side comparison of key features:.

Number of Connected Devices
The number of devices on your network plays a big role in your decision:
- Fewer than 10 devices: If your household has minimal connected tech—just basic web browsing and streaming—Wi-Fi 5 can still deliver solid performance.
- 10 or more devices: With smartphones, laptops, TVs, game consoles, and smart devices all competing for bandwidth, Wi-Fi 6's ability to manage simultaneous connections becomes a major advantage.
- Smart homes: Homes loaded with smart lights, cameras, thermostats, and sensors will benefit from Wi-Fi 6's efficiency in handling many devices at once.
Internet Speed
Consider how fast your internet plan is—and how fast it might become:
- Under 500 Mbps: Wi-Fi 5 can usually keep up with modest service plans.
- 500 Mbps and up: If you're on gigabit internet or planning to upgrade, Wi-Fi 6 helps you take full advantage of that speed.
- Future-proofing: Planning to upgrade your internet plan in the next couple of years? Wi-Fi 6 ensures you're ready.
Home Size and Layout
Your physical space affects how far and how well your Wi-Fi reaches:
- Smaller homes/apartments (under 1,500 sq ft): Wi-Fi 5 should be sufficient in compact spaces with minimal obstacles.
- Larger homes (1,500+ sq ft): Wi-Fi 6's range and dual-band support (including the longer-reaching 2.4 GHz band) help ensure better coverage.
- Multi-story homes: Wi-Fi 6 routers—or mesh systems—tend to provide stronger coverage across floors.
Even in a Wi-Fi 6 setup, some devices benefit from a wired connection. For high-priority uses like gaming or desktop workstations, a wired router still delivers the most stable and consistent connection.
Budget Considerations
Your budget may guide your decision, but don't forget to factor in long-term value:
- Wi-Fi 5 gear is typically more affordable, with decent routers starting around $50–$100.
- Wi-Fi 6 routers start closer to $150–$200, with premium models climbing higher.
- Value over time: While Wi-Fi 6 costs more upfront, its better performance and longevity may make it the smarter buy if you don't upgrade networking equipment often.
Looking Ahead: Wi-Fi 7 and Beyond
Wi-Fi technology never stands still, and the recently introduced Wi-Fi 7 standard (802.11be) is already generating excitement. With compatible devices starting to enter the market now in 2025 and becoming more widespread through the end of the year and into 2026,
Wi-Fi 7 promises the following enhancements:
- Top Speeds: Potentially up to 46 Gbps, nearly five times the maximum speeds of Wi-Fi 6.
- Wider Channels: 320 MHz channel bandwidth, offering twice the data throughput compared to Wi-Fi 6.
- Improved Reliability: Multi-Link Operation (MLO) reduces latency by enabling simultaneous connections across multiple frequency bands.
- Greater Efficiency: Advanced modulation (4096-QAM) helps handle more devices simultaneously and efficiently.
Even with Wi-Fi 7's advancements, it's important to keep things in perspective. Early Wi-Fi 7 hardware tends to be pricier, and you'll need compatible client devices, such as smartphones or laptops, to fully benefit. You can shop our full range of Wi-Fi 7 access points, Wi-Fi 7 routers, and more networking essentials at your local Micro Center. If your current Wi-Fi 5 or Wi-Fi 6 setup already meets your needs, there's no rush. But being aware of what's coming next ensures you're ready when the time is right to upgrade your network.
Final Thoughts on Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6
Choosing between Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 comes down to how many devices you have, how you use them, and how future-ready you want your home network to be. Wi-Fi 5 may still be a solid option for simple setups, but for most modern households—especially those with smart devices, gamers, remote workers, or gigabit internet—Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 offer a smoother, faster, and more efficient experience.
Ready to level up your connectivity? Explore Micro Center's full range of networking equipment to find the best gear for your setup and budget. Stay tuned, we'll be releasing a full article going into detail on Wi-Fi 7 very soon.
Image Credits
AlexanderTrou/Shutterstock.com
PST Vector/Shutterstock.com
dencg/Shutterstock.com
Comment on This Post
See More Blog Categories
Recent Posts
How-To
Everything You Need to Know About WiFi 7
From dual-band basics to multi-gigabit speeds, WiFi has come a long way, and WiFi 7 is the most transformative leap yet. Whether you're powering a smart home, streaming in 8K, gaming in real time, or working from the cloud, this new standard is designed for how we use the internet today.
Continue Reading About Everything You Need to Know About WiFi 7
News
Micro Center Launches In-Store Game Console Repair Service
The new service, starting in a four-city pilot program, will fix common problems on PlayStation, Xbox and Nintendo consoles, from broken drives to HDMI ports.
Continue Reading About Micro Center Launches In-Store Game Console Repair Service